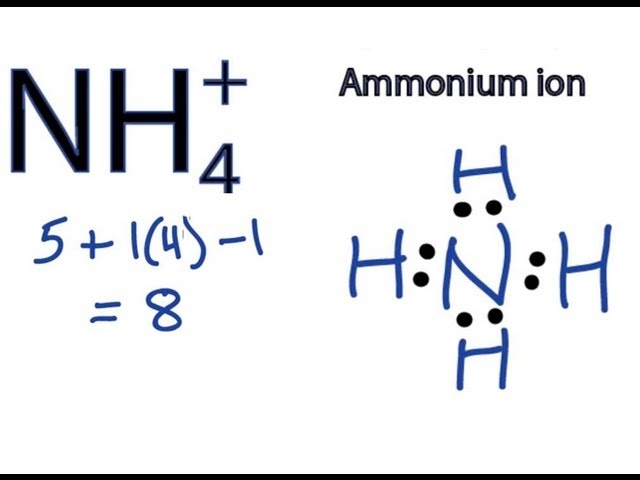
Lewis Diagram for NH4+
A Lewis diagram, also known as an electron dot diagram, is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom or molecule. It shows the arrangement of electrons in the outermost shell of the atom or molecule. Lewis diagrams are used to predict the chemical bonding behavior of atoms and molecules. Lewis diagrams are a helpful way to understand the structure of atoms, molecules, and ions. They can be used to predict the chemical bonding between atoms and to determine the shape of molecules.
Here are steps on how to create a Lewis diagram for NH4+:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons. Nitrogen (N) has five valence electrons, and each hydrogen (H) atom has one valence electron. The ammonium ion (NH
4+) has a +1 charge, which means it has lost one electron. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons is 5 + 4(1) – 1 = 8. Place the least electronegative atom in the center. In NH4+, nitrogen is the least electronegative atom, so it is placed in the center. Connect the atoms with single bonds. Single bonds are formed by sharing two electrons between two atoms. Distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs. The remaining electrons are distributed as lone pairs on the nitrogen atom. Check the octet rule. The octet rule states that atoms are most stable when they have eight valence electrons. In NH4+, the nitrogen atom has eight valence electrons, and each hydrogen atom has two valence electrons.
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ is shown below:
H:N:H H:H
Benefits of using Lewis diagrams:
- Lewis diagrams can be used to predict the chemical bonding behavior of atoms and molecules.
- Lewis diagrams can be used to determine the shape of molecules.
- Lewis diagrams can be used to understand the electronic structure of atoms and molecules.
Tips for creating Lewis diagrams:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons.
- Place the least electronegative atom in the center.
- Connect the atoms with single bonds.
- Distribute the remaining electrons as lone pairs.
- Check the octet rule.
Lewis diagrams are a helpful tool for understanding the structure and bonding of atoms and molecules.
Lewis Diagram for NH4+: Key Aspects
A Lewis diagram is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom or molecule. It shows the arrangement of electrons in the outermost shell of the atom or molecule. Lewis diagrams are used to predict the chemical bonding behavior of atoms and molecules.
- Structure: The Lewis diagram for NH4+ shows the arrangement of the valence electrons in the ion.
- Bonding: The Lewis diagram shows that the nitrogen atom in NH4+ is bonded to each of the four hydrogen atoms by a single bond.
- Electrons: The Lewis diagram shows that the nitrogen atom in NH4+ has eight valence electrons, which satisfies the octet rule.
- Shape: The Lewis diagram can be used to predict the shape of the NH4+ ion, which is tetrahedral.
- Charge: The Lewis diagram shows that the NH4+ ion has a +1 charge, which is due to the loss of one electron from the nitrogen atom.
- Reactivity: The Lewis diagram can be used to predict the reactivity of the NH4+ ion. The ion is a weak acid and can donate a proton to a base.
- Solubility: The Lewis diagram can be used to predict the solubility of NH4+ compounds. NH4+ compounds are generally soluble in water.
- Applications: NH4+ is used in a variety of applications, including fertilizers, explosives, and food additives.
These key aspects of the Lewis diagram for NH4+ provide a deeper understanding of the structure, bonding, and properties of this important ion.
Structure
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ provides crucial information about the structure of the ion. It shows that the nitrogen atom is bonded to each of the four hydrogen atoms by a single bond. This arrangement of atoms and bonds gives the NH4+ ion its characteristic tetrahedral shape.
- Bonding: The Lewis diagram shows that the nitrogen atom in NH4+ is bonded to each of the four hydrogen atoms by a single bond. These single bonds are formed by the sharing of two electrons between the nitrogen and hydrogen atoms.
- Shape: The Lewis diagram can be used to predict the shape of the NH4+ ion. The tetrahedral shape of the ion is due to the fact that the nitrogen atom is bonded to four other atoms.
- Charge: The Lewis diagram shows that the NH4+ ion has a +1 charge. This charge is due to the loss of one electron from the nitrogen atom.
- Reactivity: The Lewis diagram can be used to predict the reactivity of the NH4+ ion. The ion is a weak acid and can donate a proton to a base.
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ provides a valuable tool for understanding the structure and bonding of this important ion. This information can be used to predict the properties and reactivity of NH4+ in different chemical reactions.
Bonding
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ shows that the nitrogen atom is bonded to each of the four hydrogen atoms by a single bond. This bonding information is crucial for understanding the structure and properties of the NH4+ ion. The single bonds between the nitrogen and hydrogen atoms indicate that the electrons are shared equally between the atoms. This equal sharing of electrons results in a stable bond between the atoms.
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ can be used to predict the shape of the ion. The tetrahedral shape of the ion is due to the fact that the nitrogen atom is bonded to four other atoms. This tetrahedral shape is important for the ion’s stability and reactivity.
The bonding information in the Lewis diagram can also be used to predict the reactivity of the NH4+ ion. The ion is a weak acid and can donate a proton to a base. This reactivity is due to the fact that the nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons that can be donated to a proton.
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ is a valuable tool for understanding the structure, bonding, and reactivity of this important ion. This information can be used to predict the properties and behavior of NH4+ in different chemical reactions.
Electrons
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ shows that the nitrogen atom has eight valence electrons. This satisfies the octet rule, which states that atoms are most stable when they have eight valence electrons. The octet rule is important because it helps to explain the chemical bonding behavior of atoms.
In the case of NH4+, the nitrogen atom has four valence electrons. Each hydrogen atom has one valence electron. When the nitrogen atom bonds with the four hydrogen atoms, it shares its four valence electrons with the hydrogen atoms. This results in each hydrogen atom having two valence electrons, which satisfies the duet rule. The nitrogen atom has four pairs of valence electrons, which satisfies the octet rule.
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ is a valuable tool for understanding the structure and bonding of this important ion. It shows that the nitrogen atom is bonded to each of the four hydrogen atoms by a single bond. This information can be used to predict the shape of the ion, which is tetrahedral. The Lewis diagram can also be used to predict the reactivity of the ion, which is a weak acid.
Shape
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ provides valuable information about the shape of the ion. The tetrahedral shape of the ion is due to the fact that the nitrogen atom is bonded to four other atoms.
- Electron-pair geometry: The Lewis diagram shows that the nitrogen atom in NH4+ has four electron pairs. These electron pairs are arranged in a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry.
- Molecular shape: The molecular shape of NH4+ is also tetrahedral. This is because the four hydrogen atoms are bonded to the nitrogen atom in a tetrahedral manner.
- Bond angles: The bond angles in NH4+ are all 109.5 degrees. This is the ideal bond angle for a tetrahedral molecule.
The tetrahedral shape of the NH4+ ion has several important implications. For example, the tetrahedral shape allows the ion to pack efficiently in crystals. The ion’s shape also affects its reactivity. For example, the tetrahedral shape of the ion makes it less likely to react with other molecules.
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ is a valuable tool for understanding the structure and bonding of this important ion. The information provided by the Lewis diagram can be used to predict the shape of the ion, which is tetrahedral. This information can be used to understand the properties and reactivity of NH4+ in different chemical reactions.
Charge
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ provides valuable information about the charge of the ion. The +1 charge on the ion is due to the loss of one electron from the nitrogen atom.
- Formation of the ion: The NH4+ ion is formed when a neutral NH3 molecule loses a proton (H+ ion). This loss of a proton results in the formation of a positive charge on the nitrogen atom.
- Stability of the ion: The +1 charge on the NH4+ ion helps to stabilize the ion. The positive charge on the nitrogen atom attracts the electrons in the N-H bonds, which helps to strengthen the bonds.
- Chemical properties of the ion: The +1 charge on the NH4+ ion affects its chemical properties. For example, the ion is a weak acid and can donate a proton to a base.
The charge information in the Lewis diagram for NH4+ is essential for understanding the structure, bonding, and reactivity of this important ion. This information can be used to predict the properties and behavior of NH4+ in different chemical reactions.
Reactivity
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ provides valuable information about the reactivity of the ion. The Lewis diagram shows that the nitrogen atom in NH4+ has a lone pair of electrons. This lone pair of electrons can be donated to a proton, which results in the formation of NH3 and H+ ions.
The reactivity of the NH4+ ion is important in many chemical reactions. For example, the NH4+ ion is used as a fertilizer. The NH4+ ion can also be used to neutralize acids. The ability of the NH4+ ion to donate a proton is also important in biological systems. For example, the NH4+ ion is involved in the transport of protons across cell membranes.
The Lewis diagram is a valuable tool for understanding the reactivity of the NH4+ ion. The Lewis diagram can be used to predict the products of reactions involving the NH4+ ion. The Lewis diagram can also be used to understand the role of the NH4+ ion in biological systems.
Solubility
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ can be used to predict the solubility of NH4+ compounds in water. The Lewis diagram shows that the NH4+ ion is a polar molecule. Polar molecules are attracted to water molecules, which are also polar. This attraction between the NH4+ ions and the water molecules results in the solubility of NH4+ compounds in water.
The solubility of NH4+ compounds in water is important for many reasons. For example, NH4+ compounds are used as fertilizers. The solubility of NH4+ compounds in water allows them to be easily taken up by plants. NH4+ compounds are also used in the production of cleaning products. The solubility of NH4+ compounds in water allows them to be easily dissolved in water and used to clean surfaces.
The Lewis diagram is a valuable tool for understanding the solubility of NH4+ compounds in water. The Lewis diagram can be used to predict the solubility of other polar molecules in water. The Lewis diagram can also be used to understand the solubility of ionic compounds in water.
Applications
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ provides valuable information about the structure, bonding, and reactivity of this important ion. This information can be used to understand the applications of NH4+ in a variety of fields.
One important application of NH4+ is as a fertilizer. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plants, and NH4+ is a readily available source of nitrogen. The Lewis diagram for NH4+ shows that the nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons, which can be donated to plants. This donation of electrons helps plants to grow and thrive.
Another important application of NH4+ is in the production of explosives. NH4+ is a component of ammonium nitrate, which is a powerful explosive. The Lewis diagram for NH4+ shows that the nitrogen atom has a positive charge, which helps to stabilize the explosive. This stability makes ammonium nitrate a safe and effective explosive for use in mining and construction.
NH4+ is also used in a variety of food additives. For example, NH4+ is used as a leavening agent in baked goods. The Lewis diagram for NH4+ shows that the nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons, which can react with acids to produce ammonia gas. This ammonia gas causes baked goods to rise.
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ is a valuable tool for understanding the applications of this important ion. The Lewis diagram can be used to predict the properties and reactivity of NH4+, which can help to improve the efficiency and safety of a variety of applications.
A Lewis diagram, also known as an electron dot diagram, is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom or molecule. It shows the arrangement of electrons in the outermost shell of the atom or molecule. Lewis diagrams are used to predict the chemical bonding behavior of atoms and molecules.
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ shows that the nitrogen atom has four valence electrons and each hydrogen atom has one valence electron. The nitrogen atom forms single bonds with each of the four hydrogen atoms. The resulting ion has a positive charge because it has lost one electron.
Lewis diagrams are important because they can be used to predict the chemical bonding behavior of atoms and molecules. They can also be used to determine the shape of molecules and to understand the electronic structure of atoms and molecules. Lewis diagrams are a valuable tool for chemists and other scientists.
FAQs about Lewis Diagrams for NH4+
Lewis diagrams are a helpful tool for understanding the structure and bonding of atoms and molecules. The Lewis diagram for NH4+ shows that the nitrogen atom has four valence electrons and each hydrogen atom has one valence electron. The nitrogen atom forms single bonds with each of the four hydrogen atoms. The resulting ion has a positive charge because it has lost one electron.
Here are some frequently asked questions about Lewis diagrams for NH4+:
Question 1: What is the Lewis structure of NH4+?
The Lewis structure of NH4+ is:
H:N:H H:H
Question 2: How many valence electrons does NH4+ have?
NH4+ has 8 valence electrons.
Question 3: What is the shape of the NH4+ ion?
The NH4+ ion has a tetrahedral shape.
Question 4: What is the hybridization of the nitrogen atom in NH4+?
The nitrogen atom in NH4+ is sp3 hybridized.
Question 5: What is the bond angle in NH4+?
The bond angle in NH4+ is 109.5 degrees.
Question 6: What is the polarity of the NH4+ ion?
The NH4+ ion is polar.
These are just a few of the most frequently asked questions about Lewis diagrams for NH4+. For more information, please consult a chemistry textbook or online resource.
Lewis diagrams are a valuable tool for chemists and other scientists. They can be used to predict the chemical bonding behavior of atoms and molecules, to determine the shape of molecules, and to understand the electronic structure of atoms and molecules.
Conclusion
The Lewis diagram for NH4+ is a powerful tool that can be used to understand the structure, bonding, and reactivity of this important ion. The Lewis diagram shows that the nitrogen atom has four valence electrons, each of which is shared with a hydrogen atom. This results in a tetrahedral-shaped ion with a positive charge. The Lewis diagram can also be used to predict the chemical bonding behavior of NH4+ and its reactivity with other molecules.
Lewis diagrams are an essential tool for chemists and other scientists. They provide a simple and visual way to understand the electronic structure of atoms and molecules. Lewis diagrams can be used to predict chemical bonding behavior, molecular shape, and reactivity. By understanding the Lewis diagram for NH4+, chemists can gain a better understanding of this important ion and its role in a variety of chemical reactions.
Youtube Video: